Viewer Navigation
All 3-D viewers in ElumTools utilize the same navigation commands. Currently this applies to the Photometric Web viewer in the Light Source - Source Position tab in Luminaire Manager and the visualization viewer.
Keyboard Shortcuts
Keyboard key stroke |
Function |
| Arrows | Navigate |
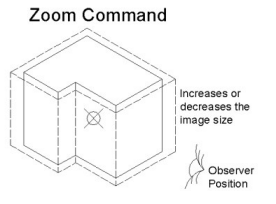
| Home | Zoom In |
| End | Zoom Out |
| Ctrl+End | Zoom Extents |
| PageUp/PageDown | Increase/Decrease navigation speed |
| Alt+Left Arrow | Previous view |
| Alt+Right Arrow | Next view |
| Ctrl+C | Copy image to the clipboard |
| Type a number (e.g., 5.5), press Enter | Sets Eye and Focus height for Interactive commands |
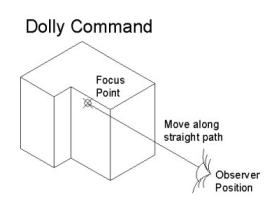
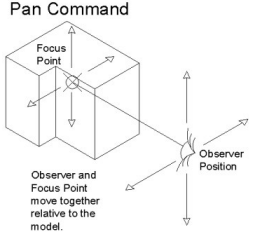
| Shift key (hold) | Changes interactive command to Pan motion |
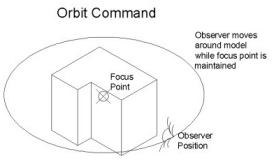
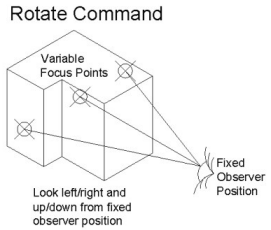
| Ctrl key (hold) | Changes interactive command to Rotate motion |

 (Previous),
(Previous),  (Next)
(Next) (Save),
(Save),  (Copy)
(Copy) Orthographic views
Orthographic views Isometric views
Isometric views Zoom Extents
Zoom Extents